Components
• 1 Arduino Uno
• 3 resistor (220 ohms)
• 3 potentiometers
• 3 LEDs (red, blue, green)
• 1 breadboard
Description
Welcome to DJ Spectrumizer. This lab project involves three potentiometers that control LEDs in three ways
- To control the color in the spectrum (Hue)
- To control the brightness of the light ( Vue)
- To control the rate at which they blink . (Beats)
Extra Credit :
A combination of these controls enables a person using the DJ Spectrumizer to set the mood of the party with the color and brightness and make the color blink based on the beats of the song he/she is playing.
I researched about the range of beats a song can have and found out that it ranges from 40bpm to 220bpm. I have used the potentiometer to map the values to this.
Code
// The three primary colour LEDs, driven as analgue outputs (actually PWM, but
// close enough for our analogue eyes).
const int ledPinRed = 11; // Red LED connected to analogue out pin
const int ledPinGrn = 10; // Green LED connected to analogue out pin
const int ledPinBlu = 9; // Blue LED connected to analogue out pin
// The Brightness potentiometer goes on an analogue pin, taking the pin from
// 0V to 5V.
const int potPinSat = 1;
// The Hue potentiometer goes on an analogue pin, taking the pin from
// 0V to 5V.
const int potPinHue = 2;
// The Beats potentiometer goes on an analogue pin, taking the pin from
// 0V to 5V.
const int potPinBeats = 3;
// Constants to define the ranges.
const int hueRedLow = 0;
const int hueRedHigh = 255;
const int hueBlue = 170;
// The size of the angle of one sector (1/6 of a colour wheel), and of a complete
// cycle of the colour wheel.
const int angleMin = 0;
const int angleSector = 60;
const int angleMax = 360;
const int brightMin = 0;
const int brightMax = 255;
//constants to define the range of beats
const int beatsMin = 40;
const int beatsMax = 220;
// Work variables.
// The hue potentiometer value is mapped to the range 0 to 360 (degrees).
int potValueHue;
//The brightness potentiometer value is mapped from 0 to 255 (full brightness)
int potValueSat;
//The beats potentiometer value is mapped from 40 to 220
int potValueBeats;
int hue, brightness;
const int saturation = 255;
// The brightess of each LED (0 to 255).
unsigned int r, g, b;
void setup() {
// Still need to set a baud rate, even for USB.
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set LED pins to output.
pinMode(ledPinRed, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPinGrn, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPinBlu, OUTPUT);
// Poteniometer analogue pin is an input.
pinMode(potPinHue, INPUT);
pinMode(potPinSat, INPUT);
pinMode(potPinBeats, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// The Hue potentiometer value is mapped to degrees - 0 to 360 - for convenience.
potValueHue = map(analogRead(potPinHue), 0, 1023, angleMin, angleMax);
// The Brightness potentiometer value is mapped to values from 0 to 255.
potValueSat = map(analogRead(potPinSat), 0, 1023, brightMin, brightMax);
//The beats potentiometer value is mapped to values from 40 to 220 bpm
potValueBeats = map(analogRead(potPinBeats),0,1023, beatsMin,beatsMax);
// Colour wheel mode (red to red, wrapped around in a cycle).
hue = map(potValueHue, angleMin, angleMax, hueRedLow, hueRedHigh);
brightness = potValueSat;
// Do the conversion.
HSBToRGB(hue, saturation, brightness, &r, &g, &b);
analogWrite(ledPinRed, r);
analogWrite(ledPinGrn, g);
analogWrite(ledPinBlu, b);
// converting beats per minute to delay
int bpmToDelay = 1000 / (220/60);
delay(bpmToDelay);
}
// This function taken from here:
// http://eduardofv.com/read_post/179-Arduino-RGB-LED-HSV-Color-Wheel-
void HSBToRGB(
unsigned int inHue, unsigned int inSaturation, unsigned int inBrightness,
unsigned int *oR, unsigned int *oG, unsigned int *oB )
{
if (inSaturation == 0)
{
// achromatic (grey)
*oR = *oG = *oB = inBrightness;
}
else
{
unsigned int scaledHue = (inHue * 6);
unsigned int sector = scaledHue >> 8; // sector 0 to 5 around the color wheel
unsigned int offsetInSector = scaledHue - (sector << 8); // position within the sector unsigned int p = (inBrightness * ( 255 - inSaturation )) >> 8;
unsigned int q = (inBrightness * ( 255 - ((inSaturation * offsetInSector) >> 8) )) >> 8;
unsigned int t = (inBrightness * ( 255 - ((inSaturation * ( 255 - offsetInSector )) >> 8) )) >> 8;
switch( sector ) {
case 0:
*oR = inBrightness;
*oG = t;
*oB = p;
break;
case 1:
*oR = q;
*oG = inBrightness;
*oB = p;
break;
case 2:
*oR = p;
*oG = inBrightness;
*oB = t;
break;
case 3:
*oR = p;
*oG = q;
*oB = inBrightness;
break;
case 4:
*oR = t;
*oG = p;
*oB = inBrightness;
break;
default: // case 5:
*oR = inBrightness;
*oG = p;
*oB = q;
break;
}
}
}
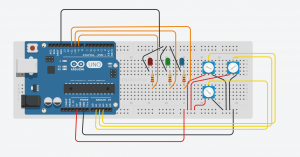
Could not show it properly in a Video. Will demonstrate it in the class.
