Alternative Data Sources in Investment Management Firms
By Peter Yi Wang | December 6, 2019
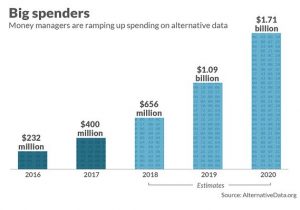
Investment management firms have found alternative data as a way to gain information advantage over their peers. Industry spending on alternative data by investment firms such as mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, private-equity firms will jump from $232 million in 2016 to a projected $1.1 billion in 2019 and $1.7 billion next year, according to AlternativeData.org, an industry trade group supported by data provider YipitData. There are currently hundreds of alternative data providers across the globe, with a heavy concentration in the United States.
In recent years, investment management firms, particularly hedge funds which are highly focused on time-sensitive information, have pioneered innovative ways of tracking information. As an example, some hedge fund may send out drones to fly over lumberyards to see the stockpile of lumbers to make the bet to short the price of lumber. Other hedge funds may retrieve satellite images of retail stores parking lots to gauge the performance of the department stores. And furthermore, other hedge funds track online job postings of different companies to decipher the trajectory of growth.
While all these methods give hedge funds a particular edge over its peers, these actions also raise questions around the privacy protection rights for the subjects of these tracking. For example, does the lumberyard owners worry that drones are flying over their yards? Does parking lot drivers concerned about satellite taking pictures of their parked cars? Does the particular management of the subject companies care that their online job postings are being scrapped?
The most urgent issue that faces the alternative data and investment management industry that uses alternative data today is the lack of a global best practices standard.
In October, 2017, the Investment Data Standards Organization (IDSO) was formed in the United States to support the growth of alternative data industry through the creation and promotion of industry standards and best practices. This non-governmental organization is focused on three main products: 1) Personal identifiable information (PII); 2) Web crawling; and 3) Dataset compliance for sensitive information (SI).
There are four main areas which can be materially enhanced from a privacy perspective:
- Consent: The data subjects like individuals (or websites containing individual information) and businesses need to consent directly or indirectly to the data collection process.
- Storage and security: The alternative data storage should have a regulatory time limit similar to call transcripts of trading records under the Securities regulations in many countries. This ensures that personal identifiable information is deleted safely under a certain period. The data subjects should also reserve the right to delete their personal data upon request.
- Secondary use: Secondary use of the alternative data should be strictly monitored or prohibited given the unfair distribution of costs and benefits.
- Confidentiality: Personal identifiable information should be kept confidential at all times and data subjects have the opt-out option to exclude their information from alternative data sets.
Given alternative data is a global phenomenon and rapidly expanding, a global standards organization similar to IDSO should be formed to address the four critical recommendations listed above. Without a proper global standard, the alternative data industry and the investment management industry that utilizes alternative data may continue to breach the privacy boundaries of data subjects. Urgent privacy protection actions are needed in the alternative data industry.
